INNOVATION – MORE BENEFITS FROM OPEN INNOVATION.
the past companies believed in closed innovation and competition with each other. However, this has changed now, and attention is being given to Open Innovation, which is the use of purposive inflows and outflow of knowledge to accelerateinnovation and expand the markets for external use onnovztion respectively. The business world today is very competitive and more open, hence there’s need for companies,businesses to be more creative and innovative to attract more customer. Open innovation helps the company to involve the consumers, employees, researchers in developing news ideas for everyones satisfaction. One thing i like about open innovation is that you dont guess on what the market wants since you are involving the in creating the new ideas but also new markets and this might reduce fhe operating cozts and increase the profits. Additionally open innovation shorten the innovation cycle and dramastically reduces the cost of research and development.

In short Open innovation is all about;
- Involving people (employees, clients, suppliers, other stakeholders) in terms of new ways of working, incentives, fading distinction between work and (social) networks;
- Operations ((e-)processes and (e-)infrastructure) in terms of (e.g.) web access, communities, facilitation of knowledge and creativity sharing;
- Policy (written and unwritten rules) regarding (e.g.) intellectual property, privacy, outside communication; and
- Culture (e.g. openness, learning, networking) to create the right (and safe) atmosphere
From this we learn that, open innovation tries to simplifiy the organisations activities by ensuring that there is a good link between all the functions, procedures and people both within and outide the organisation. However having the great ideas is not enough, it is important that the ideas which have been generated should be implementaed by the company to the satisfaction of the customers. So it is important for companies to ready for soem changes in their strategies according to the vission and the ideas which have been generated.
There are several companies which are using open innovation and one of them is Cadbury whic is a company that believes in creating strong relationship with suppliers, universities, SME’s and other multinational organisations that lead to great innovation and products.Here is a link for the companies open innovation websites www.collaboration.cadbury.com. The premise for these initiatives are, that no one organization or human being can know everything. “The world is becoming too fast, too complex and too networked for any company to have all the answers inside,” Yochai Benkler wrote in ” The wealth of Networks”
There is also a platorm for different companies known as Atizo, where companies companies can post a question to a crowd to get more and better solutions. This is called also Open 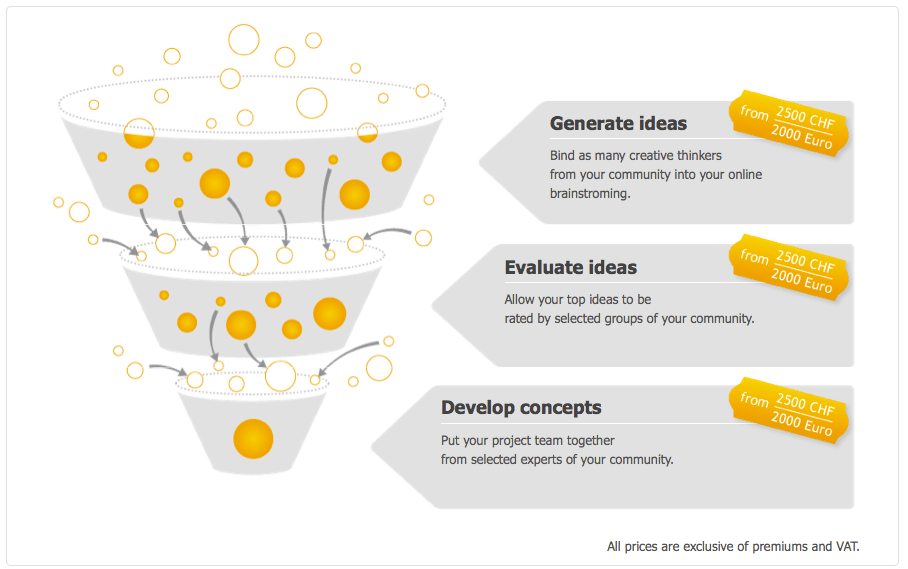 innovation since you are not looking inside your own firm for ideas but to a broader spectrum of people. Some call it crowd sourcing for ideas. Atizo’s platform allows companies to generate ideas, evaluate ideas and develop the ideas into marketable concepts. Most companies have seen the benefits of the plat form saying it is fast and cheap.
innovation since you are not looking inside your own firm for ideas but to a broader spectrum of people. Some call it crowd sourcing for ideas. Atizo’s platform allows companies to generate ideas, evaluate ideas and develop the ideas into marketable concepts. Most companies have seen the benefits of the plat form saying it is fast and cheap.
Other known initiatives are My Starbucks Idea, Dell IdeastormIBM Innovation Jam and Shell GameChanger. These are all corporate examples of Open Innovation. For R&D matters more organizations are beginning to post challenges on Innocentive which is a platform where companies post challenges and pay for researchers around the globe to solve them. Procter & Gamble is one of the active players on Innocentive.
Reference
Leaders Lab, http://leaderlab.com/open-innovation/
Wikipedia (2011) Open Innovation, http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Innovation
http://www.ideavents.com/
INNOVATION – MORE BENEFITS FROM OPEN INNOVATION.
the past companies believed in closed innovation and competition with each other. However, this has changed now, and attention is being given to Open Innovation, which is the use of purposive inflows and outflow of knowledge to accelerateinnovation and expand the markets for external use onnovztion respectively. The business world today is very competitive and more open, hence there’s need for companies,businesses to be more creative and innovative to attract more customer. Open innovation helps the company to involve the consumers, employees, researchers in developing news ideas for everyones satisfaction. One thing i like about open innovation is that you dont guess on what the market wants since you are involving the in creating the new ideas but also new markets and this might reduce fhe operating cozts and increase the profits. Additionally open innovation shorten the innovation cycle and dramastically reduces the cost of research and development.

In short Open innovation is all about;
- Involving people (employees, clients, suppliers, other stakeholders) in terms of new ways of working, incentives, fading distinction between work and (social) networks;
- Operations ((e-)processes and (e-)infrastructure) in terms of (e.g.) web access, communities, facilitation of knowledge and creativity sharing;
- Policy (written and unwritten rules) regarding (e.g.) intellectual property, privacy, outside communication; and
- Culture (e.g. openness, learning, networking) to create the right (and safe) atmosphere
From this we learn that, open innovation tries to simplifiy the organisations activities by ensuring that there is a good link between all the functions, procedures and people both within and outide the organisation. However having the great ideas is not enough, it is important that the ideas which have been generated should be implementaed by the company to the satisfaction of the customers. So it is important for companies to ready for soem changes in their strategies according to the vission and the ideas which have been generated.
There are several companies which are using open innovation and one of them is Cadbury whic is a company that believes in creating strong relationship with suppliers, universities, SME’s and other multinational organisations that lead to great innovation and products.Here is a link for the companies open innovation websites www.collaboration.cadbury.com. The premise for these initiatives are, that no one organization or human being can know everything. “The world is becoming too fast, too complex and too networked for any company to have all the answers inside,” Yochai Benkler wrote in ” The wealth of Networks”
There is also a platorm for different companies known as Atizo, where companies companies can post a question to a crowd to get more and better solutions. This is called also Open  innovation since you are not looking inside your own firm for ideas but to a broader spectrum of people. Some call it crowd sourcing for ideas. Atizo’s platform allows companies to generate ideas, evaluate ideas and develop the ideas into marketable concepts. Most companies have seen the benefits of the plat form saying it is fast and cheap.
innovation since you are not looking inside your own firm for ideas but to a broader spectrum of people. Some call it crowd sourcing for ideas. Atizo’s platform allows companies to generate ideas, evaluate ideas and develop the ideas into marketable concepts. Most companies have seen the benefits of the plat form saying it is fast and cheap.
Other known initiatives are My Starbucks Idea, Dell IdeastormIBM Innovation Jam and Shell GameChanger. These are all corporate examples of Open Innovation. For R&D matters more organizations are beginning to post challenges on Innocentive which is a platform where companies post challenges and pay for researchers around the globe to solve them. Procter & Gamble is one of the active players on Innocentive.
Reference
Leaders Lab, http://leaderlab.com/open-innovation/
Wikipedia (2011) Open Innovation, http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Innovation
http://www.ideavents.com/
Rural Development: Land misuse
In this post I would like to tackle the issue of land misuse or as some may call it mismanagement and to show how is it related to food waste and respectively food security. People are used to think of problems in a very superficial way. We are not willing to understand the whole production process. For instance when we think about wind energy we think of a carbon free electricity source, but we don’t think about its production that emits quite a lot. The same thing happens with food. If I would ask an average person where does the food come from, the answer would be probably: “from the supermarket”. An average person may

Total arable land by country.
not be conscious of the whole chain that the “tomato” has to overcome to be eaten. At the beginning of this chain there is choosing a right place to grow, cultivate or breed future nutrition.
The main problem that I wanted to highlight is the relation of land misuse and food waste. It is quite logical. In developed countries we are running out of land. In most of those countries around 40% of land is used for agriculture. If around 1/3 of the food produced is being wasted, it means that 13.3% of the land is used for nothing. Not mentioning the fact that somebody’s work is being not respected. But this is another problem.
The next issue related to this is the fact that a lot of food wasted in rich countries has, what Tristram Stuart called, a low resources to calories ratio. These are tomatoes, dairy products and meat that need a big amount of resources as land, water or fuel. On the graph showed on the left side, we can see land use in the USA. 41% of land is used for grazing, while forests cover  only 22%! “For example, it takes an average of around 31 million kcal of primary energy input to grow a tonne of tomatoes with a calorific content of just 170,000 kcal. By contrast, it takes just 600,000 kcal of primary energy to grow a tonne of bread-wheat, which contains 3-3.5 million kcal, an energy input/output ratio 918 times higher”. (Stuart, T., 2009) This example shows us what have to be considered, if we are thinking of a sustainable development. Each country should plan their food supply in advance taking into account all the resources needed. What is also crucial is to influence people diet habits, behaviors and general awareness. We as consumers have to know, how food that we are eating was made and how we are influencing the whole food system.
only 22%! “For example, it takes an average of around 31 million kcal of primary energy input to grow a tonne of tomatoes with a calorific content of just 170,000 kcal. By contrast, it takes just 600,000 kcal of primary energy to grow a tonne of bread-wheat, which contains 3-3.5 million kcal, an energy input/output ratio 918 times higher”. (Stuart, T., 2009) This example shows us what have to be considered, if we are thinking of a sustainable development. Each country should plan their food supply in advance taking into account all the resources needed. What is also crucial is to influence people diet habits, behaviors and general awareness. We as consumers have to know, how food that we are eating was made and how we are influencing the whole food system.
Another crucial problem are centralized big farms, from which corporations own a significant part. Regardless its big contribution to world food production there is still around billion people living in hunger, so quick solutions are needed. A recent analysis of adaptation work in Uganda has shown that small-scale agriculture is beneficial. First of all it can be easily and almost immediately implemented. As it is small-scale agricultures are working for them and know that if they won’t work well their harvest will be respectively low. Problems are solved on a local level, so their contribution to the environment is higher. For this project the main issue was soil and water conservation, which has reduced the planting costs by 75%. Moreover, the environment has also
One of big crop farms
benefited from farmers actions. Using fewer chemical fertilizers and pesticides soil and water conditions have improved significantly. In addition to that, local farmers have become self-sufficient, what has highly encouraged other people to follow that model.
Maybe it is naïve to think that such actions could be implemented everywhere, but it is good to know that it is possible. Of course it will be extremely difficult or even impossible to break the current food system that is defended by world superpowers. However, people are becoming more and more aware of what is happening around them and I believe that we are slowly moving to a more sustainable food system. Nonetheless there is a lot to be done and following the example of researches such as the above may be crucial for our further development.
References:
1. Stuart, T., 2009, “Waste – Uncovering the Global Food Scandal”
2. Munang, R. and Nkem, J.N., 2011, “Using Small-Scale Adaptation Actions to Address the Food Crisis in the Horn of Africa: Going beyond Food Aid and Cash Transfers.”
3. “Land in America” retrieved from http://www.thegreenworkplace.com/2008/08/land-in-america.html
4. Grywacheski, A., 2011, “Arable Land” retrieved from http://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~umgrywac/PLNT4600/mini1/mini1.1.html
CDM in China: promoting development?
Clean Development Mechanism should be a great alternative to comply with emissions reduction obligations under the Kyoto protocol for Annex I countries, while promoting sustainable development where most needed.
Fundamental condition for projects to be applied are consequently the impossibility of “self-development” for the host country at the same conditions offered by the project (principle of additionality) and the assurance of improving development conditions, globally and locally where the project is implemented.
Such conditions in my opinion are at least doubtful in the Fujian Niutoushan Hydropower Project, promoted by VITOL S.A, Switzerland, and hosted by China. The project involve the construction of a 100MW Hydropower plant, which involve a dam to gain pressure for the turbines to run efficiently.
More obvious doubt come up considering that China to me looks very promising in its own possibility to design and implement hydropower project, both economically and technologically. Just to give a figure, in the year of project implementation, “China was the largest hydropower producer and is expected to continue to lead global hydro use in the coming years”(World Watch Institute). Actually China is having an impressive boom in capacity added by renewables, with hydropower accounting for an additional 16 GW in 2010, expected to be plus 140 GW by 2015.
Moreover, Hydropower is well known to be among the cheapest forms of producing energy, being already competitive against fossils fuels power plants.
In terms of economic development, the impact of the project in the region is practically null, as it is experiencing alone a great development (+12% in 2010), with plenty of foreign enterprises already investing in the area and with a big share occupied by technology firms. Also the GDP per capita is above the average in China.
When considering social development, it appears difficult to believe that a technology among the cheapest in term of maintenance costs can assure long term employment in the area, not to mention that construction phases usually create more distress than benefits as the big amount of people employed are cast-off after few months.
Additionally (and practically in all CDM projects), the reservation about the use of the revenues by the recipient company (or government) remains unsolved: there are no tracking mechanisms assuring that the money won’t be used in unsustainable projects.
A last consideration about the carbon credits transferred thanks to the tonnes of CO2e avoided: there is no understandable reason to my view to assign credits for a period of 7 years (as stated by the PDD of the project), as the scenario of CO2 emissions from energy sector can totally change during the considered period, given China’s potential.
An interesting summary about CDM risks is provided by the following video:
Rural Development – Access to Water in Rural Areas
According to the International Fund for Agricultural Development IFAD, one third of the population experiences physical or economic water scarcity. This problem is especially harsh in the sub-Saharan Africa and in South Asia. In the continuous competition among different sectors (households, agriculture, industries, energetic) for water, the most affected are the rural populations.
Providing water for agricultural productivity and domestic uses is critical for achieving food security and improved rural livelihoods. Access to water is also deeply linked to poverty, health, nutrition and land distribution. In general, water is basic for achieving progress in rural regions.
There are several difficulties related to water access that should become governmental priorities. Structural problems such as poor infrastructure, fair tariff water systems and water quality part of the problem. Among the problems that can be addressed by local authorities and communities are: inefficient irrigation systems, lack of water storage, water wastage and pollution and lack of education on proper water management.
 How to provide access to water in a sustainable way?
How to provide access to water in a sustainable way?
One of the strategies that can help solve this problem is infrastructure improvement. Among infrastructure projects that can be carried out by the government or private companies are building reservoirs and rainwater harvesting tanks. Irrigation systems are basic for improving efficiency. For example converting them into multiuse water service systems can help improve water use. Investment on infrastructure provides employment and therefore a better quality of life. It is directly linked to research and development of new agriculture and water management technologies.
Providing a fair tariff system can be another possible solutions to guarantee equity in water distribution. Regional studies should be carried out to determine how water is distributed among economic levels and new prices should be established so that everyone has access. Governments should even study the possibility of providing subsidies to the lowest income communities.
Access to information and community participation are also crucial aspects. Involvement of communities ensures having a real picture of how water is used and guarantees that people participate in new programs. Populations should be aware of all the activities, improvements and policies. Empowering communities with microcredits with appropriate monitoring measures can be a good alternative to promote change. Since 2/3 of the communities that suffer water scarcity are women, they are a key part of the solution. Women are main actors for agriculture, domestic hygiene and industry. If governments establish legislation that allows women to own land a sense of ownership and a better water management can be created. Participation of women in decision-making processes might be helpful because they can help to identify current problems and possible solutions.
Improving water efficiency is one of the most important challenges, which implies water productivity in agriculture and creating a water saving culture. Prioritizing the use of water by reallocating water from lower-value, to higher-value uses can constitute an option. This must be done with education and in a way that nobody looses. If taxes for water waste are imposed to companies, awareness and efficiency can significantly increase.
Finally, training and education are basic to achieve water access. Courses regarding to water management, crop switching, water wastage and recycling, organic fertilizers and preventing water contamination should be implemented. Community coordination, incentives and constant monitoring are success measures that should be considered.
In order to enhance agricultural productiveness and if we want to achieve the goal of producing 2 times more food by 2030, water access must improve. No strategy would be successful without a regulatory framework for sustainable and equitable water distribution and management. A safe water system requires competitive institutions that provide, administer, educate and monitor the appropriate use of water in rural areas, and, without education and community involvement no significant changes can be expected.
|
Successful water access programs Commune agro-ecosystems analysis Cambodia – Participatory approach designed to help communities improve decision-making. Significantly improved fisheries productiveness. Farmer associations to address the needs urban producers Sri Lanka – Farmer field schools – Internal Loans – Social security schemes – documentation for water management. Water storage India – WMI researchers and partners have been experimenting different combinations of ponds and tanks so that farmers can store and manage water to maximize benefits. Incomes have increased by 20%. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Nepal – project to improve nutrition among women through increased access to irrigation water. |
Sources
Gender and Water. Securing water for improved rural livelihoods: The multiple-uses system approach. December 2007. IFAD. More information: http://www.ifad.org/gender/thematic/water/gender_water.pdf
Rural Water Supply & Sanitation Initiative. African Developing bank Group. More information: http://www.afdb.org/en/topics-and-sectors/initiatives-partnerships/rural-water-supply-sanitation-initiative/
South Africa: Lack of Water Access Undermining Rural Development. AllAfrica, June 8, 2011. More information: http://allafrica.com/stories/201106080928.html
Water for a Food-Secure World. International Water Management Institute. Annual Report 2010. More information: http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/About_IWMI/Strategic_Documents/Annual_Reports/2010/Annual_Report_2010.pdf
Open and lead user innovation
Innovation. This word refers to a wide range of meanings. Nowadays, it seems to be a new imperative for business success. However, innovate is a unique human’s capability and it has been par of our whole history, and for so of the business’ history.
Nowadays, the challenges have change. Business should know how to take advantage of the spectacular informational network that has been created, thanks to the social media and technological advances. At the same time, companies should find the way to differentiate from the competitors, in a way that they could create and add value to consumers. And here is where innovation comes to the main stage.

A business can innovate at every stage. Innovation could be understood as a process, as a management approach, as cultural values, or just as the final product. Among different approaches, there are two that deserve our attention.
The lead User Innovation takes advantage of what is done; it helps to create new ideas (using existing products, services or process), to solve problems. “Lead users are users whose present strong needs will become general in a marketplace months or years in the future” (von Hippel 1986). In fact, lead users “job” is to give solutions to problems (or necessities) with higher impact, using products that already available. In some cases, they develop new products that attend their own necessities, so the become innovators. This method allows a better understanding of the customers’ necessities, expectations, and preferences. “Products that lead users develop often become the basis for important commercial products when lead user needs become mainstream.”
The Open Innovation is a method related to the break of boundaries; to “open” and “listen” what the others can say about your business, including, the competence. “Open innovation is a paradigm that assumes that firms can and should use external ideas as well as internal ideas, and internal and external paths to market, as the firms look to advance their technology” (Chesbrough, 2003). The idea is to accelerate internal innovation through openly sharing (in both directions) knowledge, research, between companies. The collaborative sprit is potential zed with this approach.
 There are many business cases about open and lead user innovation. For example, FINISH is an initiative that believes that financial inclusion could improve sanitation health. Their aim is to innovate in the sanitation technology in a way that address and solve the health problems in most of the developing countries. They use the Open innovation method to identify ideas, potential partners, etc., based on the ideaken platform. See the video! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sWB1IbmNcdw
There are many business cases about open and lead user innovation. For example, FINISH is an initiative that believes that financial inclusion could improve sanitation health. Their aim is to innovate in the sanitation technology in a way that address and solve the health problems in most of the developing countries. They use the Open innovation method to identify ideas, potential partners, etc., based on the ideaken platform. See the video! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sWB1IbmNcdw
References: (all consulted by 10/02/12)
Chesbrough, H.W. (2003). Open Innovation: The new imperative for creating and profiting from technology. Boston: Harvard Business School Press
Revised paper published as: von Hippel, Eric (1986) “Lead Users: A Source of Novel Product Concepts,” Management Science 32, no. 7 (July):791-805.
http://leaduser.com/
http://www.finishsociety.com/
Case Study of Las Rozas. Locking for an implementation of SIA and EIA
This is an issue that affects my environment and me directly. I live in an area where it supposed to be well know however as you are going to see it is suffering a huge environmental problem related with water sanitation. An implementation of a Strategic Impact Assessement or an Environmental Impact Assessment in the urban planning of all the areas affected would have avoided this huge problem.
As a result of hypertrophy urban sanitation networks in many towns of Spain are in a state of increasing saturation that generates a generalized deficit in some cases extremely situations that is having serious consequences for environmental and public health.
This state deficit in the sewerage system is in many cases the hidden face of the massive housing development, often aimed at homes that are advertised as luxury and yet have network sanitation of a third World country. Las Rozas de Madrid is a city paradigmatic of this situation. Its population has increased almost 1,500% over the last twenty years and now claims 2,500% wound to the new urban planning.
These channels come of the sewer deficit of their own neighborhoods, municipal sewage or saturated or malfunction, and in other cases of direct discharges of the same municipality or in discharging the rivers from other municipalities such as Torrelodones and Galapagar that pass through Las Rozas.
Now we have to face the case of a municipality crossed by numerous streams that should be dry however instead of that the most part of the year they are sewage channels of the whole municipality. Most of the streams and floodplains of Las Rozas are contaminated. In some cases we can find new streams that has arisen because of the overload of the other sewage channels. The major part of this waste has been produced continuously for over 15 years. It is not difficult to see sludge sedimented in the channels contaminated.
Since 8 years ago there are evidence of repeated complaints from the neighbors and different communities of Las Rozas such as Molino de la Hoz, Monte Rozas and Parque Rozas however the municipality in rarely situation is taking action in order to solve the problem. The municipality have not started any kind of large-scale renovation which is a serious dereliction of duties from the administration as well as the autonomic one which is responsible for the safety in terms of urbanism and environment of the citizens.
References:
www.slavemoslasrozas.org
Climate Change thought…..
Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement signed to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC, Convention). The goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The set forth timeframe is 2008 until 2012. Involvement of countries is voluntary. Currently, the USA is pursuing a separate climate change strategy unlinked to the international climate change policies. It is imperative that success is reached in the reduction of greenhouse gases from both from an environmental and economic standpoint. International trading regimes will encourage US to engage in an international regime. If the Kyoto parties decide to recognize credits generated from emission reduction projects of non parties such as the US (along the same lines as the clean development mechanism) this will lead to the realization of a more global goal for battling climate change. The US could potentially make use of low cost emissions reductions and recognize them aiding to the reduction of emissions. It is unlikely that the Kyoto Protocol will produce a single emissions trading system. The emergence of various trading systems is sure to arise with the same intention of reducing GHG emissions, which will surely bring about considerable challenges. It is important that Kyoto parties allow for credits of non involved members. The most important thing is that globally, we work to reduce GHG emissions.
The pros of the KyotoProtocol
– It sets GHG emissions reduction targets – The largest known contribution comes from the burning of fossil fuels, which releases carbon dioxide gas to the atmosphere. – IPCC Fourth AssessmentReport: Climate Change 2007:http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg1/en/faq-2-1.html)
– The protocol invents economically justified mechanisms to reduce GHG emissions
The cons
– The existing Kyoto Protocol is signed and ratified by certain amount of countries. The total percentage of Annex I Parties (developed countries) emissionsis 63.7%. (http://unfccc.int/kyoto_protocol/status_of_ratification/items/2613.php). As the result –the countries which are responsible for great part of the word’s emissions have no obligation according to the Kyoto Protocol.
– Fast growing economies like China, India are among the developing countries which have no obligations according to the Kyoto protocol and practically can continue to develop without implementing environmental technologies and emitting great amount of GHG.
– Some countries which are historically responsible for climate change(for example developed countries with economy in transition, like Ukraine) in fact have no obligation to reduce GHG as in 1990 (base year in the KyotoProtocol) they emitted much more emissions than in 2008-2012 because of the bigeconomy recession after 1990′s. (NECU, 2010: http://www.necu.org.ua/wp-content/uploads/ghg_potential_uk_final.pdf).As the result Ukraine has an opportunity to develop and increase the level of GHG emission.
– Controlling schemes of Kyoto Protocol flexible mechanisms implementation are not perfect. There are examples when Kyoto revenues, received from assigned amount units trading between different states are spent on different purposes which do not lead to GHG emission reduction and are not even connected with environmental issues. Thus implementations of the Kyoto Protocol flexible mechanisms do not lead to GHG emission reduction and realization of the purpose of the UNFCCC.
-Without mechanisms to ensure the effective enforcement and compliance with international obligations, the commitment to mitigate climate change is basically void.
– The issue of the compliance and legal consequences. Protocols to the Convention should develop mechanisms of GHG emissions reduction and aim at establishing transparent monitoring and verifying rules.
Open Innovation: VOTE TO GET MOVING AND SHAKING
Ideas que generan ideas: IDEO.
IDEO es una firma de innovación con sede en Palo Alto, California. Buscando expandirse luego del éxito obtenido, ésta creó una base datos que aplicase la innovación desde una perspectiva pública, es decir, que los aportes que se hicieran a un determinado proyecto vinieran de los miembros de la página porque precisamente los proyectos también estaban públicos.
El funcionamiento de esta base de datos va de la siguiente manera: Un proponente brinda su idea de manera pública (en ocasiones, son casos ya en ejecución pero que siempre pueden mejorar), los inscritos en la página van aportando soluciones y de toda la tormenta de ideas de seleccionan las que mejor responden al problema. Esta modalidad de innovación se le conoce como Innovación Abierta, precisamente porque se construye con base en las ideas que se vayan generando de personas que no necesariamente pertenecen al proyecto en un principio, permitiendo cierto grado de inclusión dentro de éstos al público en general. La gran ventaja de este sistema es que personas de múltiples disciplinas aportan sugerencias, soluciones, y en múltiples ocasiones los nuevos aportes se apoyan de los comentarios ya publicados, dándole forma a las ideas y perfeccionando lo que ya existe. Nada es creado de la nada, todo existe porque hay algo que lo hace existir…
Un proyecto interesante que ganó la propuesta de OpenIDEO sobre cómo hacer un canal de conexión para generar impactos sociales positivos en las comunidades, o sino que éstos quedaran registrados en la plataforma, fue el de una estudiante (Charlotte Fliegner) radicada en Melbourne, Australia, la cual sugirió que se usase esta plataforma para crear puentes entre profesores, estudiantes, universidades y clientes que anduviesen haciendo algún proyecto de construcción. El funcionamiento de la idea se basa en la proposición de conceptos por parte de los estudiantes, entre los cuales resultarían seleccionados algunos de éstos. Una vez que el proceso de selección culminase, las universidades buscarían un proyecto donde estas ideas pudiesen materializarse en la práctica, convirtiéndolas en innovadoras en este sentido. Dichos conceptos podrían insertarse en las materias ofrecidas dentro de las universidades con ejemplos prácticos, levantando información para el mundo de la arquitectura que pudiese compartirse y sustentarse con casos reales.
Aún cuando es claro que la Innovación Abierta permite ventajas como ver fuera de la caja, con enfoques multidisciplinarios, económicamente conveniente porque nace de la voluntad de quien tenga un espíritu abierto para sencillamente aportar positivamente a cualquier proyecto, es claro que no siempre pueden aplicarse a cualquier proyecto o problema. Es cierto también que quien conoce bien un problema, puede que tenga los elementos para darle soluciones. Dentro de las empresas la inclusión de los empleados en las problemáticas resulta fundamental en este sentido, ya que son quienes están a diario viviendo con los reveses y tienen información suficiente sobre éstos. Es el mismo principio para ambos tipos de innovación: Desde lo existente es que puede innovarse.
En conclusión, la Innovación Abierta es un elemento multiplicador de las soluciones, Jamás tenemos las respuestas para todo, por lo que hay que permitir que a la hora de cambiar, las propuestas sean suficientes para explorar la mejor opción. OpenIDEO es un claro ejemplo de cómo una plataforma genera aún más innovación y solución, y así lo prueba Charlotte Fliegner habiendo usado esa herramienta. Si bien la Innovación abierta es una manera ventajosa de producir cambio, no es menos cierto que la innovación puede venir desde nosotros mismos para nosotros mismos, y he ahí la importancia de la inclusión de los colaboradores de una empresa en moldear las soluciones que corresponden a ésta generar.
Charlotte Fliegner (2010). Carlotte Fliegner. Disponible en: http://www.openideo.com/profiles/charlottefl/ . Consultado el 11/02/2012.
Wikipedia (2011). IDEO. Disponible en: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IDEO . Consultado el 11/02/2012.
IDEO (Sin Fecha). OpenIDEO. About Us. Disponible en: http://www.openideo.com/about-us . Consultado el 11/02/2012.
OpenIDEO (2011). How might we increase social impact with OpenIDEO over the next year? Disponible en: http://www.openideo.com/open/impact/realisation/realisation-project-openuni/ . Consultado el 11/02/2012.



![CDM Backdropweb[1]](https://www.eoi.es/blogs/francescomazzeo/files/2012/02/CDM-Backdropweb1.jpg)








.png)
].gif)
.png)
].png)
].png)
].png)
.png)
].png)
.png)
